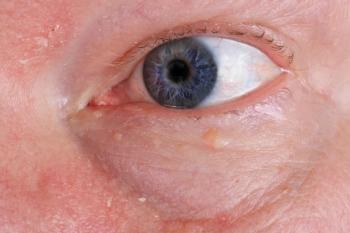
New study finds collarettes more common in patients with moderate-to-severe DED
Researchers performed a secondary analysis of the DREAM study data.
In utilizing the Dry Eye Assessment and Management (DREAM) study (NCT02128763) data, a team of researchers found that lid margin collarettes were common in patients with moderate-to-severe dry eye disease (DED), but a majority of those patients’ collarettes did not progress over time. Additionally, there was no association found between collarettes and dry eye symptoms.1,2
Researchers were led by Alexander E. Azar of Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine in Cleveland, Ohio.1
“Though DED signs were significantly more severe in eyes with collarettes, not all signs were linearly associated with greater collarette severity,” the researchers stated. “Scores for eyelid erythema (P < .001), TBUT [tear breakup time] (P < .001), MGD [meibomian gland dysfunction] grade (P = .01), and overall composite DED severity score (P = .01) became more severe as the severity of collarettes increased.... Conjunctival staining, corneal staining, and Schirmer test were not significantly associated with collarette severity (all P > .05). Tear osmolarity was unexpectedly better as collarette severity increased.”
Researchers performed a secondary analysis of the DREAM study data, which was a multicenter, double-blinded clinical trial that evaluated omega-3 supplementation in patients with moderate-to-severe DED. A total of 535 patients were involved in the study, and they were randomly assigned 2:1 to either an active omega-3 supplement group or an olive oil placebo. All patients were followed over the full 12 months of the study.1,2
Dry eye symptoms were assessed with the Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI) and ocular discomfort, with the signs recorded through conjunctival staining, corneal staining, TBUT, the Schirmer test, and the MGD grade. Signs and symptoms were then compared by collarette presence and severity at visits at baseline and months 3, 6, and 12.1,2
Collarette presence data were documented by evaluating lid margin debris in both upper and lower eyelids for each eye, and were graded on a scale of normal to very severe. Normal was defined as 0 collarettes, mild as 1 to 5 collarettes, moderate as 6 to 20 collarettes and a few fragments, severe as 21 to 40 collarettes and 1 to 2 clumps, and very severe as over 40 collarettes and more than 3 clumps.1,2
At baseline, 699 (65%) of eyes had no collarettes, 300 (28%) had mild, and 71 (7%) had moderate; no eyes were recorded to have severe or very severe collarettes at baseline. At the 6- and 12-month visits, a small number of patients were reported to have severe and very severe collarettes. Additionally, DED signs were reported to be significantly more severe in eyes with collarettes, as evident in a high composite DED severity score in the collarette group (0.51 vs 0.49; P = .03).1
Of the dry eye signs analyzed, presence of collarettes was associated with worse scores for eye lid erythema (18.6% vs 12.2% with moderate or severe eyelid erythema; P < .001), corneal staining (5.06 vs 4.59; P = .01), TBUT (3.24 vs 3.54 s; P = .01), and Schirmer test score (7.92 vs 8.63; P = .04),” the researchers reported. “The presence of collarettes was not significantly associated with conjunctival staining score (P = .41) and MGD grade (P = .12). Collarettes were associated with an unexpectedly better tear osmolarity (304.3 vs 307.0; P = .01).”
Additionally, a significant association between collarettes and rosacea was found. Additionally, White and non-Hispanic patients with moderate-to-severe DED were found to be more likely to have collarettes. However, the authors recommended that additional research be conducted to “determine the underlying cause of the association between race and collarettes, including the role of skin phototype, genetics, and other potential confounders.” Researchers also noted the study’s limitations in the lack of description of the collarette type.1
References
Azar AE, Haddad EN, Augello PA, et al; Dre Eye Assessment and Management (DREAM) Study Research Group. Association between lid margin collarettes and dry eye disease severity in the Dry Eye Assessment and Management (DREAM) study. Eye (Lond). Published online November 25, 2025.
doi:10.1038/s41433-025-04105-5 Dry Eye Assessment and Management Study (DREAM). ClinicalTrials.gov. Updated July 19, 2022. Accessed November 26, 2025.
https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02128763
Newsletter
Want more insights like this? Subscribe to Optometry Times and get clinical pearls and practice tips delivered straight to your inbox.